
Go to the source code of this file.
Function Documentation
◆ secp256k1_keypair_create()
| int secp256k1_keypair_create | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_keypair * | keypair, | ||
| const unsigned char * | seckey ) |
Compute the keypair for a secret key.
Returns: 1: secret was valid, keypair is ready to use 0: secret was invalid, try again with a different secret Args: ctx: pointer to a context object, initialized for signing. Out: keypair: pointer to the created keypair. In: seckey: pointer to a 32-byte secret key.
Definition at line 195 of file main_impl.h.
◆ secp256k1_keypair_pub()
| int secp256k1_keypair_pub | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_pubkey * | pubkey, | ||
| const secp256k1_keypair * | keypair ) |
Get the public key from a keypair.
Returns: 1 always. Args: ctx: pointer to a context object. Out: pubkey: pointer to a pubkey object. If 1 is returned, it is set to the keypair public key. If not, it's set to an invalid value. In: keypair: pointer to a keypair.
Definition at line 223 of file main_impl.h.

◆ secp256k1_keypair_sec()
| int secp256k1_keypair_sec | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| unsigned char * | seckey, | ||
| const secp256k1_keypair * | keypair ) |
Get the secret key from a keypair.
Returns: 1 always. Args: ctx: pointer to a context object. Out: seckey: pointer to a 32-byte buffer for the secret key. In: keypair: pointer to a keypair.
Definition at line 213 of file main_impl.h.
◆ secp256k1_keypair_xonly_pub()
| int secp256k1_keypair_xonly_pub | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | pubkey, | ||
| int * | pk_parity, | ||
| const secp256k1_keypair * | keypair ) |
Get the x-only public key from a keypair.
This is the same as calling secp256k1_keypair_pub and then secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_from_pubkey.
Returns: 1 always. Args: ctx: pointer to a context object. Out: pubkey: pointer to an xonly_pubkey object. If 1 is returned, it is set to the keypair public key after converting it to an xonly_pubkey. If not, it's set to an invalid value. pk_parity: Ignored if NULL. Otherwise, pointer to an integer that will be set to the pk_parity argument of secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_from_pubkey. In: keypair: pointer to a keypair.
Definition at line 233 of file main_impl.h.
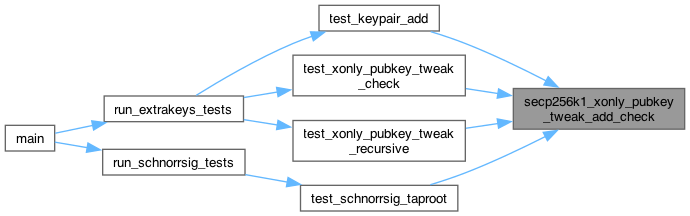
◆ secp256k1_keypair_xonly_tweak_add()
| int secp256k1_keypair_xonly_tweak_add | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_keypair * | keypair, | ||
| const unsigned char * | tweak32 ) |
Tweak a keypair by adding tweak32 to the secret key and updating the public key accordingly.
Calling this function and then secp256k1_keypair_pub results in the same public key as calling secp256k1_keypair_xonly_pub and then secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_tweak_add.
Returns: 0 if the arguments are invalid or the resulting keypair would be invalid (only when the tweak is the negation of the keypair's secret key). 1 otherwise.
Args: ctx: pointer to a context object initialized for verification. In/Out: keypair: pointer to a keypair to apply the tweak to. Will be set to an invalid value if this function returns 0. In: tweak32: pointer to a 32-byte tweak. If the tweak is invalid according to secp256k1_ec_seckey_verify, this function returns 0. For uniformly random 32-byte arrays the chance of being invalid is negligible (around 1 in 2^128).
Definition at line 254 of file main_impl.h.
◆ secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_cmp()
| int secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_cmp | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| const secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | pk1, | ||
| const secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | pk2 ) |
Compare two x-only public keys using lexicographic order
Returns: <0 if the first public key is less than the second >0 if the first public key is greater than the second 0 if the two public keys are equal Args: ctx: a secp256k1 context object. In: pubkey1: first public key to compare pubkey2: second public key to compare
Definition at line 58 of file main_impl.h.


◆ secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_from_pubkey()
| int secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_from_pubkey | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | xonly_pubkey, | ||
| int * | pk_parity, | ||
| const secp256k1_pubkey * | pubkey ) |
Converts a secp256k1_pubkey into a secp256k1_xonly_pubkey.
Returns: 1 always.
Args: ctx: pointer to a context object. Out: xonly_pubkey: pointer to an x-only public key object for placing the converted public key. pk_parity: Ignored if NULL. Otherwise, pointer to an integer that will be set to 1 if the point encoded by xonly_pubkey is the negation of the pubkey and set to 0 otherwise. In: pubkey: pointer to a public key that is converted.
Definition at line 98 of file main_impl.h.
◆ secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_parse()
| int secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_parse | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | pubkey, | ||
| const unsigned char * | input32 ) |
Parse a 32-byte sequence into a xonly_pubkey object.
Returns: 1 if the public key was fully valid. 0 if the public key could not be parsed or is invalid.
Args: ctx: a secp256k1 context object. Out: pubkey: pointer to a pubkey object. If 1 is returned, it is set to a parsed version of input. If not, it's set to an invalid value. In: input32: pointer to a serialized xonly_pubkey.
Definition at line 21 of file main_impl.h.

◆ secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_serialize()
| int secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_serialize | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| unsigned char * | output32, | ||
| const secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | pubkey ) |
Serialize an xonly_pubkey object into a 32-byte sequence.
Returns: 1 always.
Args: ctx: a secp256k1 context object. Out: output32: a pointer to a 32-byte array to place the serialized key in. In: pubkey: a pointer to a secp256k1_xonly_pubkey containing an initialized public key.
Definition at line 43 of file main_impl.h.

◆ secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_tweak_add()
| int secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_tweak_add | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| secp256k1_pubkey * | output_pubkey, | ||
| const secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | internal_pubkey, | ||
| const unsigned char * | tweak32 ) |
Tweak an x-only public key by adding the generator multiplied with tweak32 to it.
Note that the resulting point can not in general be represented by an x-only pubkey because it may have an odd Y coordinate. Instead, the output_pubkey is a normal secp256k1_pubkey.
Returns: 0 if the arguments are invalid or the resulting public key would be invalid (only when the tweak is the negation of the corresponding secret key). 1 otherwise.
Args: ctx: pointer to a context object initialized for verification. Out: output_pubkey: pointer to a public key to store the result. Will be set to an invalid value if this function returns 0. In: internal_pubkey: pointer to an x-only pubkey to apply the tweak to. tweak32: pointer to a 32-byte tweak. If the tweak is invalid according to secp256k1_ec_seckey_verify, this function returns 0. For uniformly random 32-byte arrays the chance of being invalid is negligible (around 1 in 2^128).
Definition at line 117 of file main_impl.h.

◆ secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_tweak_add_check()
| int secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_tweak_add_check | ( | const secp256k1_context * | ctx, |
| const unsigned char * | tweaked_pubkey32, | ||
| int | tweaked_pk_parity, | ||
| const secp256k1_xonly_pubkey * | internal_pubkey, | ||
| const unsigned char * | tweak32 ) |
Checks that a tweaked pubkey is the result of calling secp256k1_xonly_pubkey_tweak_add with internal_pubkey and tweak32.
The tweaked pubkey is represented by its 32-byte x-only serialization and its pk_parity, which can both be obtained by converting the result of tweak_add to a secp256k1_xonly_pubkey.
Note that this alone does not verify that the tweaked pubkey is a commitment. If the tweak is not chosen in a specific way, the tweaked pubkey can easily be the result of a different internal_pubkey and tweak.
Returns: 0 if the arguments are invalid or the tweaked pubkey is not the result of tweaking the internal_pubkey with tweak32. 1 otherwise. Args: ctx: pointer to a context object initialized for verification. In: tweaked_pubkey32: pointer to a serialized xonly_pubkey. tweaked_pk_parity: the parity of the tweaked pubkey (whose serialization is passed in as tweaked_pubkey32). This must match the pk_parity value that is returned when calling secp256k1_xonly_pubkey with the tweaked pubkey, or this function will fail. internal_pubkey: pointer to an x-only public key object to apply the tweak to. tweak32: pointer to a 32-byte tweak.
Definition at line 134 of file main_impl.h.